(Pic Credits - keycdn.com)
In the world of technology, network latency is a term that you may have heard of, but not fully understood. It can be a frustrating issue that affects the performance of your applications, and ultimately your business. In this blog, we will explore what network latency is, how it can impact your business, and what you can do to reduce it.
What is Network Latency?
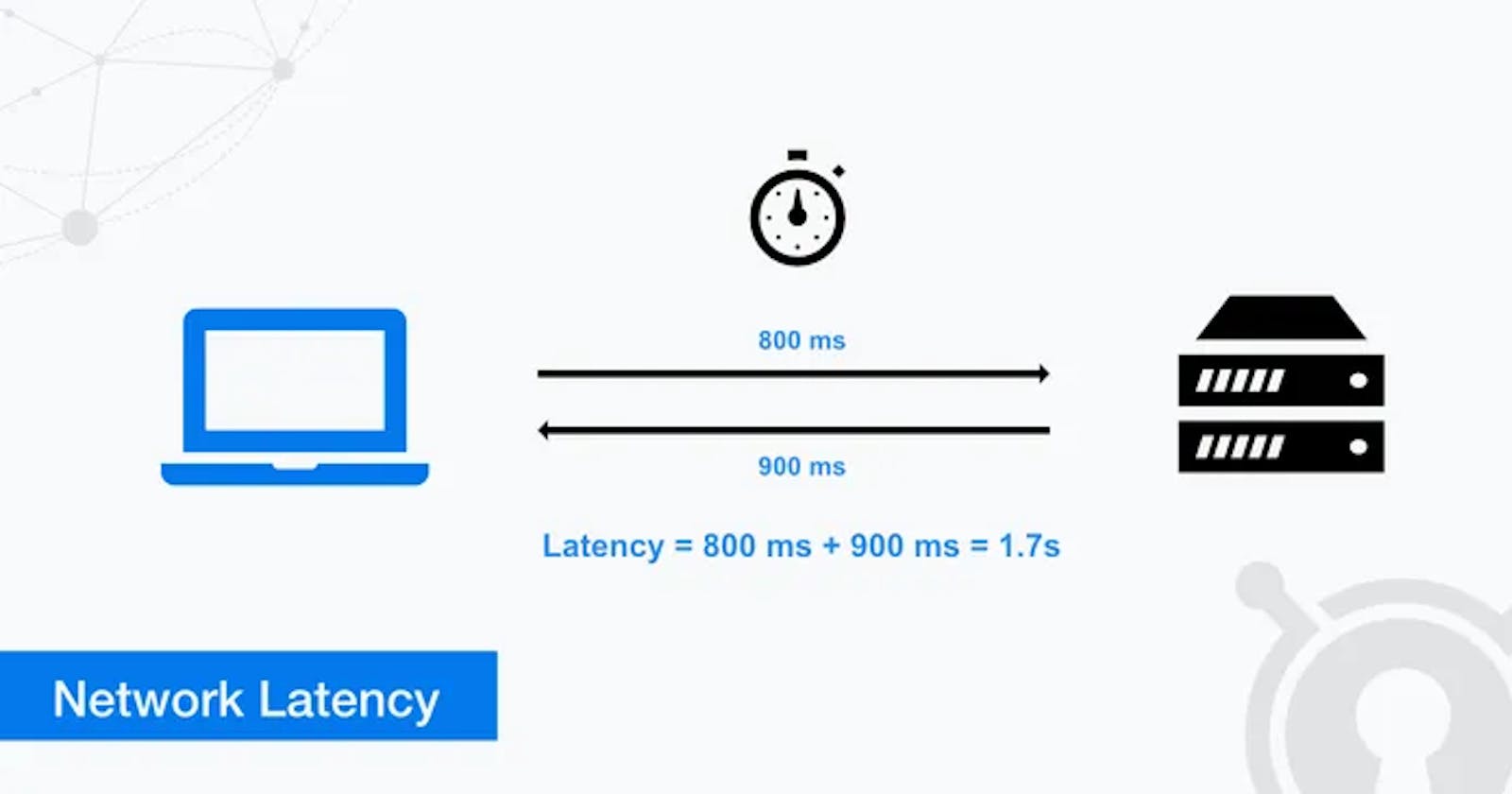
Network latency refers to the delay that occurs when data is transmitted between two devices on a network. It is often described as the time it takes for a packet of data to travel from the source to the destination. Latency is measured in milliseconds (ms) and is typically caused by network congestion, slow processing times, or physical distance between devices.
1 ms = 0.001 Seconds
dipak.patil@BETWA:~$ ping 8.8.8.8
PING 8.8.8.8 (8.8.8.8) 56(84) bytes of data.
64 bytes from 8.8.8.8: icmp_seq=1 ttl=118 time=7.49 ms
64 bytes from 8.8.8.8: icmp_seq=2 ttl=118 time=9.26 ms
64 bytes from 8.8.8.8: icmp_seq=3 ttl=118 time=7.03 ms
64 bytes from 8.8.8.8: icmp_seq=4 ttl=118 time=6.79 ms
64 bytes from 8.8.8.8: icmp_seq=5 ttl=118 time=7.00 ms
https://www.cloudping.info/ - Use this page to measure latency from your browser to various cloud provider datacenters.
How Does Network Latency Impact Your Business?
Latency can have a significant impact on your business in several ways. It can cause delays in data transfer, which can impact productivity and disrupt critical business processes. This can result in frustrated employees, dissatisfied customers, and lost revenue. In addition, high latency can lead to poor user experience, which can negatively impact your brand reputation and customer loyalty.
Reducing Network Latency
Reducing network latency is essential for businesses that rely on technology to support their operations. Here are some ways you can reduce network latency:
Use a Content Delivery Network (CDN): A CDN is a network of servers that are distributed around the world. By caching content on multiple servers, a CDN can reduce the physical distance that data needs to travel, which can reduce latency.
Optimize Your Network: You can optimize your network by using a quality of service (QoS) solution, which prioritizes traffic to reduce network congestion. You can also use a network monitoring tool to identify and resolve network issues that contribute to latency.
Use Cloud Computing: Cloud computing allows you to store and process data on servers located closer to your users. This can reduce the physical distance that data needs to travel, which can reduce latency.
Use a Load Balancer: A load balancer distributes network traffic across multiple servers to reduce congestion and improve performance. This can help reduce latency by distributing network traffic more efficiently.
In this article, we will discuss the different types of network latency and how they affect network performance.
Transmission Latency: This type of latency is caused by the time it takes for a device to send data to the network. It includes the time it takes to convert the data from a bitstream into electrical or light signals and to transmit them over the network. Transmission latency is usually very low and can be minimized with the use of high-speed data links and optimized network configurations.
Processing Latency: Processing latency is the delay that occurs when a network device receives a packet and must perform operations on it before forwarding it to its destination. This includes operations such as decryption, routing, and error detection and correction. Processing latency can be minimized by using high-speed processors and optimized network configurations.
Queueing Latency: This type of latency is caused by the time it takes for a packet to wait in a queue before being transmitted. Queueing latency can occur when a network device has more packets to send than it can handle at once. This can result in delays and dropped packets, which can degrade network performance. Queueing latency can be minimized by optimizing network configurations and increasing network bandwidth.
Propagation Latency: Propagation latency is the delay that occurs due to the physical distance between the source and destination of a data packet. This type of latency is caused by the time it takes for the packet to travel through the transmission medium, such as fiber optic cable or wireless signals. Propagation latency is directly proportional to the distance between the source and destination and can be minimized by using high-speed data links or by reducing the physical distance between the devices.
Application Latency: Application latency is the delay that occurs due to the time it takes for an application to process and respond to user requests. This includes the time it takes for a user to input data, for the application to process it, and for the application to respond to the user. Application latency can be minimized by optimizing the application code, using faster processors, and optimizing network configurations.
Network latency is an important metric to monitor in any network infrastructure to ensure smooth and reliable communication between devices. There are various tools available in the market that can help monitor network latency.
Here are the top 10 network latency tools:
Ping: Ping is a popular command-line tool used to test network connectivity and measure network latency. It sends a series of ICMP packets to a target device and measures the response time.
MTR: MTR, or My Traceroute, is a network diagnostic tool that combines the functionality of traceroute and ping. It continuously sends packets to a target device, measures the response time and provides detailed network path information.
Traceroute: Traceroute is a network diagnostic tool that identifies the path taken by packets from the source to the destination device. It measures the response time at each hop and helps identify network latency issues.
Wireshark: Wireshark is a packet capture and analysis tool used to analyze network traffic. It helps identify network latency issues by providing detailed packet-level analysis.
Netalyzr: Netalyzr is a web-based tool that analyzes network performance and provides detailed information about latency, jitter, packet loss, and other network metrics.
SmokePing: SmokePing is a network latency monitoring tool that measures latency and packet loss over time. It generates graphs and alerts when latency exceeds a specified threshold.
Nagios: Nagios is a popular network monitoring tool that provides alerts for network latency and other performance issues. It monitors network devices and services and generates notifications when thresholds are exceeded.
SolarWinds Network Performance Monitor: SolarWinds Network Performance Monitor is a comprehensive network monitoring tool that provides real-time visibility into network performance, including network latency. It provides detailed analytics and reporting features.
Zabbix: Zabbix is an open-source network monitoring tool that provides real-time monitoring of network performance, including network latency. It provides alerts and reporting features.
Datadog: Datadog is a cloud-based monitoring platform that provides real-time visibility into network performance, including network latency. It provides detailed analytics, alerting, and reporting features.
Conclusion
Network latency can be a frustrating issue for businesses that rely on technology to support their operations. By understanding what network latency is, how it impacts your business, and what you can do to reduce it, you can ensure that your applications and critical business processes run smoothly. With the right tools and strategies in place, you can minimize the impact of network latency on your business and improve overall performance.
By understanding the different types of network latency and how they affect network performance, network administrators can take steps to minimize latency and improve network performance. This can include optimizing network configurations, using high-speed data links, and reducing the physical distance between network devices. By minimizing latency, network administrators can ensure that their network delivers the fast and reliable performance that users demand.
Depending on your specific needs, some of these tools may be more suitable for your organization than others.